So, generally speaking, failover / failback is not so hard to achieve with IP SLA and tracking, but tracking feature support delayed timers of 0 to 180seconds, which is way below of what I need. Has anyone faced the same task and how was it resolved? Here's a basic config. Ip sla 99 icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source-interface Loopback180 tag Local ISP. Apply the the following IP SLA tracking and default router configuration on FW-VPN02. #sla monitor 20 type echo protocol ipIcmpEcho 100.100.100.1 interface outside-isp01 num-packets 3 frequency 10 #sla monitor schedule 20 life forever start-time now #track 1 rtr 20 reachability #route outside-isp01 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 200.200.200.2 track 1 #route. If anyone can provide some insight it would be greatly appreciated. This is an old configuration we don't use anymore. Track 10 ip sla 1 reachability delay down 10 up 10. Ip sla 1 icmp-echo 216.240.171.130 source-ip 10.0.1.1 timeout 10000 frequency 15. Ip sla schedule 1 life forever start-time now ip sla enable reaction-alerts logging esm.
Cisco Load Balancing with Failover setup example
There is Cisco router of 7200 series with four FastEthernet interfaces (FE) and a pair of serial ports. It ought to act as load balancer and failover for square measurea network|LAN|computer network} connected thereto via one atomic number 26 1/0 interface whereas 2 identical web connections are reaching to atomic number 26 0/0 and atomic number 26 0/1 (let’s name these connections as ISP_1 and ISP_2).
No dynamic routing protocols square measure utilized by ISPs however solely static routing. the first task is to make sure fast failover between 2 web connections thus square measurea network|LAN|computer network} users are mechanically switched to ISP_2 if ISP_1 fails and the other way around. once each ISP_1 and ISP_2 square measure on-line the traffic of computer network users ought to be shared between 2 links to double offered information measure on transmission (Tx) and downlink (Rx), in different words the router ought to be organized for load equalization between the links.
Load equalization setup description
There are 2 basic choices available: per-destination or per-packet load equalization. Since ISP_1 and ISP_2 connections have virtually constant link characteristics as well as delay, interference and information measure, it’s affordable plan to select per-packet possibility. compared to per-destination load equalization approach per-packet uses additional router’s hardware resources however makes it attainable to share traffic between connections additional equally. For higher forwarding performance the router are organized for Cisco specific Forwarding or just CEF per-packet load equalization.
Failover description
Every thirty seconds the router can ping 2 informatics addresses through ISP_1 and 2 alternative informatics addresses via ISP_2. If each IPs via ISP_1 becomes unapproachable (we assume that ISP_1 association fails during this case) the router can delete ISP_1’s route from its routing table therefore ISP_2 becomes the sole net association for computer network users. in the meantime the router still continues pinging 2 ISP_1’s informatics addresses and once they become accessible back ISP_1 is more to ISP_2 as a vigorous net association link. Such failover situation works in completely constant manner for ISP_2. typically this can be affordable plan to ping informatics addresses of every provider’s DNS servers once watching convenience of every ISP.
Miscellaneous details
Notice that CEF per-packet load balancing requires IOS version of 12.0+ while failover setup described above needs 12.4+ IOS version so you have to make sure your Cisco router runs at least 12.4 version of operating system. E.g. c7200-ik9o3s-mz.124-12c.bin would be ok.
Cisco router’s configuration with comments
Cisco IOS IP SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a tool that can be used to generate synthetic network traffic used for network management. SLA can be configured to send TCP connects, ICMP or even UDP packets. These packets can be used to measure metrics to ensure you are getting the performance you expect.
One of the simplest, yet most valuable, SLA configurations is ICMP. Cisco SLA can be configured to send ICMP packets to a remote device to ensure you are getting an appropriate latency across a link. For our example this is exactly what we will be looking at.
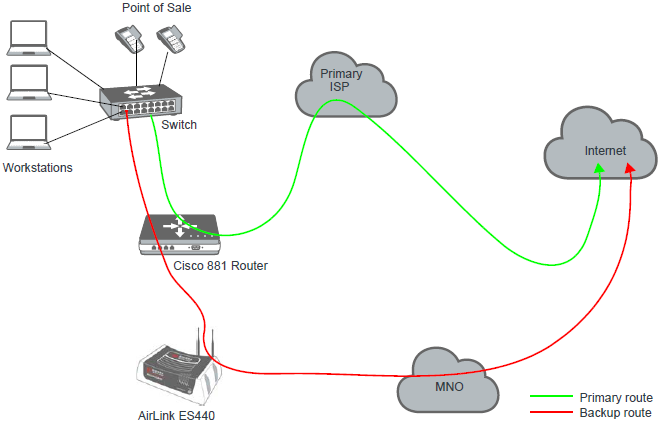
Our topology for this will be as follows:
Configuration Tasks:
- Create SLA Session
- Define SLA Traffic Type
- Define SLA destination.
- Configure SLA frequency.
- Configure SLA Schedule
- Review Configuration
- Monitor Statistics
1. ip sla 1
With the above command we configure an SLA session number of “1”.
2. icmp-echo 10.242.126.21
Cisco Asa Failover Configuration Example
Above we define that we want to use icmp-echo traffic type and our destination is 10.242.126.21
3. frequency 5
Failover Ip Address
Here we define the frequency, in seconds, of 5. This means that ICMP packets will be sent every 5 seconds to 10.242.126.21.
4. ip sla schedule 1 life forever start-time now
With this command we set the schedule for the SLA monitor to use. We have specified that the schedule for SLA 1 should run for a lifetime of forever and should start immediately, “now”.
5. show ip sla configuration
IP SLAs Infrastructure Engine-II
Entry number: 1
Owner:
Tag:
Type of operation to perform: icmp-echo
Target address/Source address: 10.242.126.21/0.0.0.0
Operation timeout (milliseconds): 5000
Type Of Service parameters: 0×0
Vrf Name:
Request size (ARR data portion): 28
Verify data: No
Schedule:
Operation frequency (seconds): 5 (not considered if randomly scheduled)
Next Scheduled Start Time: Start Time already passed
Group Scheduled : FALSE
Randomly Scheduled : FALSE
Life (seconds): Forever
Entry Ageout (seconds): never
Recurring (Starting Everyday): FALSE
Status of entry (SNMP RowStatus): Active
Threshold (milliseconds): 5000 (not considered if react RTT is configured)
Distribution Statistics:
Number of statistic hours kept: 2
Number of statistic distribution buckets kept: 1
Statistic distribution interval (milliseconds): 20
History Statistics:
Number of history Lives kept: 0
Number of history Buckets kept: 15
History Filter Type: None
Above we are able to review our configuration for the SLA monitor 1.
6. show ip sla statistics
IPSLAs Latest Operation Statistics
IPSLA operation id: 1
Type of operation: icmp-echo
Latest RTT: 3 milliseconds
Latest operation start time: 17:15:40.203 EDT Sat Aug 18 2012
Latest operation return code: OK
Number of successes: 481
Number of failures: 0
Operation time to live: Forever
Here we can see the information we can hold over our ISP’s head. We can see that we have send 481 ICMP packets and they have been successful, we have had no failures and our latest RTT was 3 ms.
Cisco IP SLA configuration has many more uses such as tracking for failover and route selection. Check out more here:
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6602/products_ios_protocol_group_home.html
—Reference fromNetworkStraining.com
More Related Cisco and Network Tips:
